首先我不做AndroidTV,只是因为一些汽车的屏幕无法触摸,所以无法获得Touch事件,但是车机上有一些旋钮,可以拿到一些键盘事件,因此需要用这些键盘事件对系统(不是应用)进行交互。所以,为了解决这个问题,就需要先了解一下Android TV应用的原理,以及键盘事件是如何传递的。
模拟Android TV
下面是最终Demo效果。
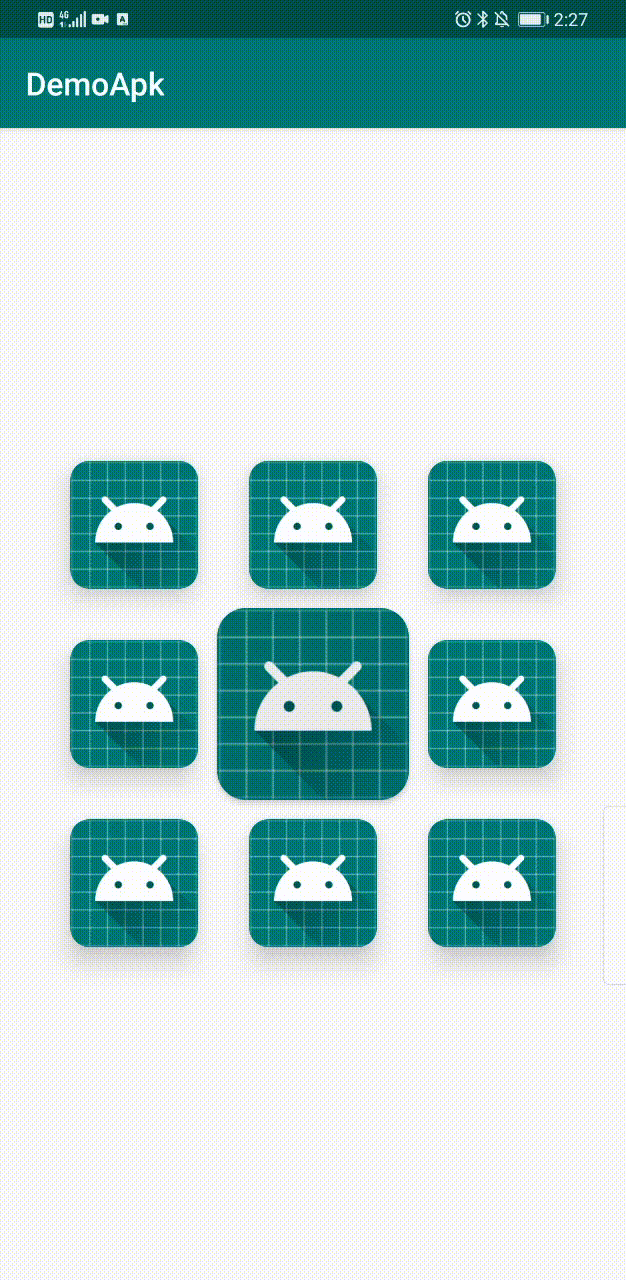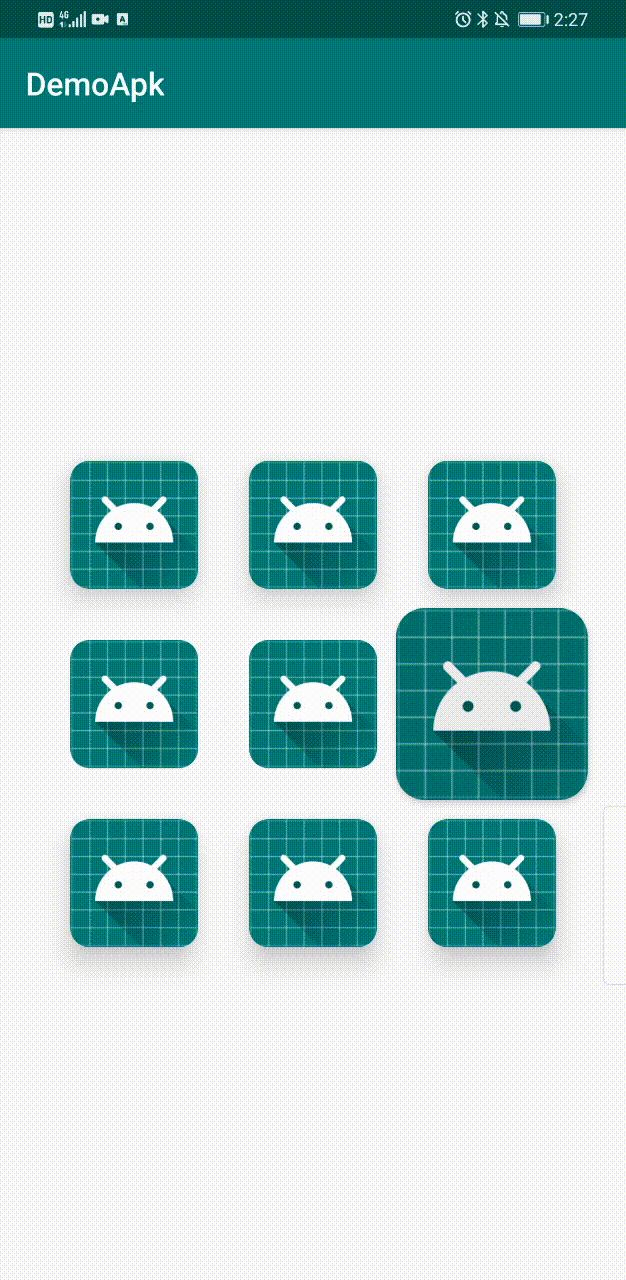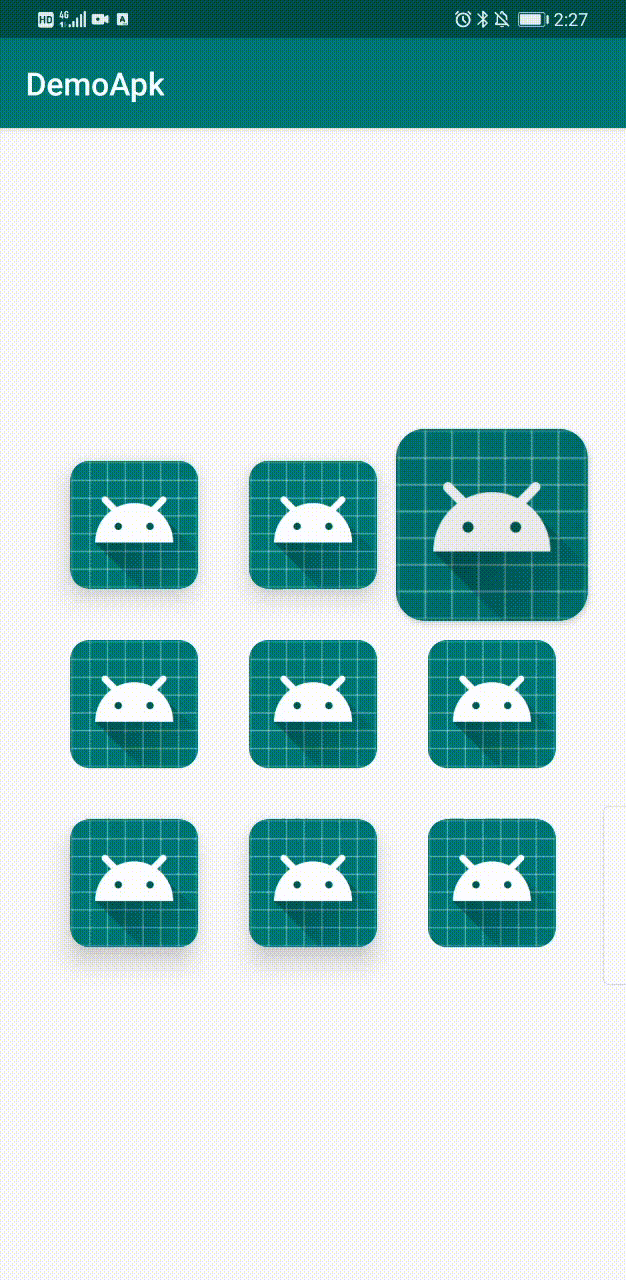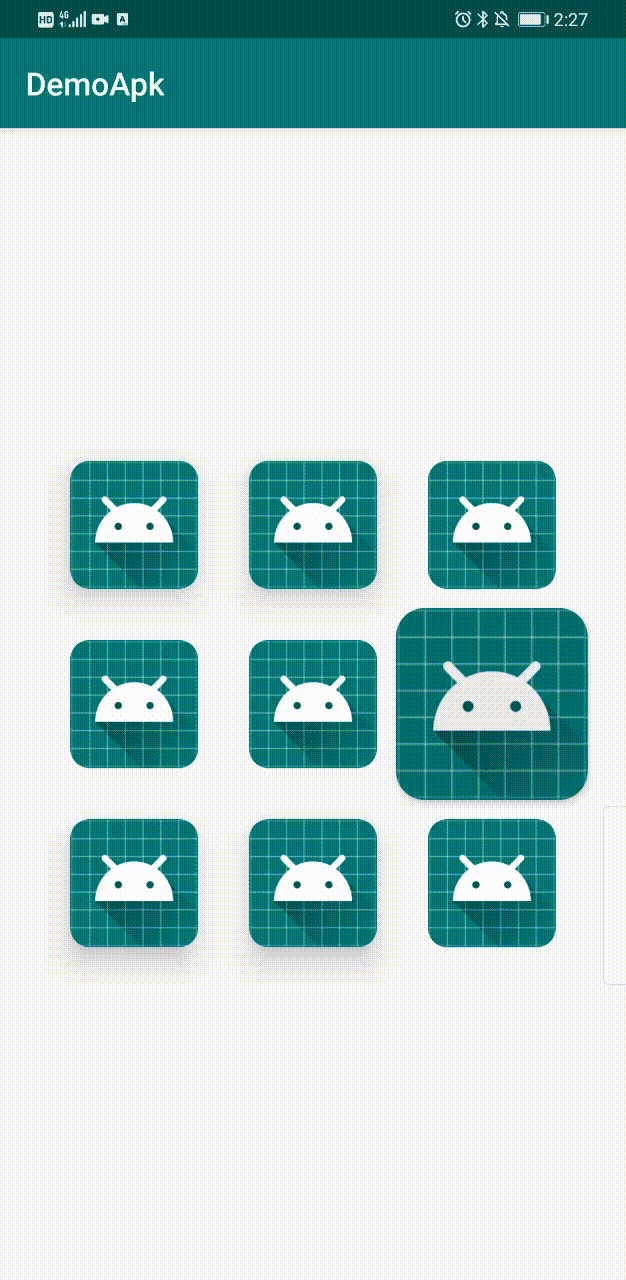
界面上有9个CardView,分布为:
1—2—3
4—5—6
7—8—9
焦点
为了使每个CardView接收焦点,所以需要设定焦点相关的属性:
android:clickable="true"
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
android:nextFocusLeft="@id/card3"
android:nextFocusRight="@id/card2"
android:nextFocusUp="@id/card7"
android:nextFocusDown="@id/card4"
也可以使用setNextFocusLeftId()方法修改焦点切换目标
设置好属性,下一步就需要实现OnFocusChangeListener接口,通过回调设置目标获得焦点之后的样式:
private void selectCard(CardView cardView, boolean selected) {
if (selected) {
cardView.setScaleX(1.5f);
cardView.setScaleY(1.5f);
cardView.setElevation(10);
} else {
cardView.setScaleX(1f);
cardView.setScaleY(1f);
cardView.setElevation(1);
}
}
整个过程并不需要处理onKeyDown回调,系统会根据xml文件里设置的前后目标去找对应的View。
所以,系统已经实现的相关的逻辑,所以就需要看看系统的实现代码。
KeyEvent事件的传递
下发KeyEvent
ViewRootImpl.ViewPostImeInputStage.processKeyEvent
private int processKeyEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final KeyEvent event = (KeyEvent)q.mEvent;
// Deliver the key to the view hierarchy.
//由dispatchKeyEvent进行焦点的分发,如果dispatchKeyEvent方法返回true,那么下面的焦点查找步骤就不会继续了。
//这里mView是Activity的顶层容器DecorView,是一FrameLayout。
//所以这里的dispatchKeyEvent方法执行的是ViewGroup的dispatchKeyEvent()方法
if (mView.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
// 是否终止事件
// 当根视图不存在就会停止下面的步骤
// 属于保护措施
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
// If the Control modifier is held, try to interpret the key as a shortcut.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& event.isCtrlPressed()
&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0
&& !KeyEvent.isModifierKey(event.getKeyCode())) {
if (mView.dispatchKeyShortcutEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
}
// Apply the fallback event policy.
// 具体实现见PhoneFallbackEventHandler中dispatchKeyEvent()方法
// 主要是对媒体键,音量键,通话键等做处理,如果是这些按键则会停止下面的步骤
if (mFallbackEventHandler.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
// Handle automatic focus changes.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
//direction用来记录方向的值,用来进行后面的焦点查找
int direction = 0;
switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
//根据指定的元状态没有按下修饰符键,则返回true
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_LEFT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_RIGHT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_UP;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_DOWN;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_TAB:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_FORWARD;
} else if (event.hasModifiers(KeyEvent.META_SHIFT_ON)) {
direction = View.FOCUS_BACKWARD;
}
break;
}
//给定了direction(遥控器按键按下的方向),接下来就是焦点寻找
if (direction != 0) {
//找到当前聚焦的View 下面会详细讲解
View focused = mView.findFocus();
if (focused != null) {
//如果focused不为空,说明找到了焦点,接着focusSearch会把direction(遥控器按键按下的方向)作为参数,找到特定方向下一个将要获取焦点的view,最后如果该view不为空,那么就让该view获取焦点。
//后面详细介绍focusSearch()具体方法
View v = focused.focusSearch(direction);
if (v != null && v != focused) {
// do the math the get the interesting rect
// of previous focused into the coord system of
// newly focused view
focused.getFocusedRect(mTempRect);
if (mView instanceof ViewGroup) {
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(
focused, mTempRect);
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetRectIntoDescendantCoords(
v, mTempRect);
}
if (v.requestFocus(direction, mTempRect)) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants
.getContantForFocusDirection(direction));
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
// Give the focused view a last chance to handle the dpad key.
if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
} else {
// find the best view to give focus to in this non-touch-mode with no-focus
View v = focusSearch(null, direction);
if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
}
}
return FORWARD;
}
当前焦点查找
View.findFocus
/**
* Find the view in the hierarchy rooted at this view that currently has
* focus.
*
* @return The view that currently has focus, or null if no focused view can
* be found.
*/
public View findFocus() {
return (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0 ? this : null;
}
ViewGroup.findFocus
在ViewGroup也有对findFocus的复写:
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see android.view.View#findFocus()
*/
@Override
public View findFocus() {
if (DBG) {
System.out.println("Find focus in " + this + ": flags="
+ isFocused() + ", child=" + mFocused);
}
if (isFocused()) {
return this;
}
if (mFocused != null) {
return mFocused.findFocus();
}
return null;
}
这里isFocused()是父类View的方法,判断代码和findFocus方法一致
/**
* Returns true if this view has focus
*
* @return True if this view has focus, false otherwise.
*/
@ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "focus")
public boolean isFocused() {
return (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0;
}
isFocused()方法的作用是判断当前view是否已经获取焦点,如果viewGroup已经获取到了焦点,那么返回本身即可,否则通过mFocused这个子view的findFocus()方法来找焦点。如果mView不是ViewGroup的话,findFocus其实就是判断本身是否已经获取焦点,如果已经获取焦点了,返回本身。
此时我们已经找到了当前获得焦点的View,接下来就是说按照给定的方向去寻找下一个即将获得焦点的view。
下一个焦点查找
View.focusSearch
前面分析到,如果某个View获取焦点,也拿到方向,就调用该方法进行查找
/**
* Find the nearest view in the specified direction that can take focus.
* This does not actually give focus to that view.
*
* @param direction One of FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, and FOCUS_RIGHT
*
* @return The nearest focusable in the specified direction, or null if none
* can be found.
*/
public View focusSearch(@FocusRealDirection int direction) {
if (mParent != null) {
return mParent.focusSearch(this, direction);
} else {
return null;
}
}
代码逻辑上看,该View并不会查找,而是通过父View进行查找
ViewGroup.focusSearch
/**
* Find the nearest view in the specified direction that wants to take
* focus.
*
* @param focused The view that currently has focus
* @param direction One of FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, and
* FOCUS_RIGHT, or 0 for not applicable.
*/
@Override
public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) {
if (isRootNamespace()) {
// root namespace means we should consider ourselves the top of the
// tree for focus searching; otherwise we could be focus searching
// into other tabs. see LocalActivityManager and TabHost for more info
return FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction);
} else if (mParent != null) {
return mParent.focusSearch(focused, direction);
}
return null;
}
判断是否为顶层布局(isRootNamespace()方法),若是则执行对应方法,若不是则继续向上寻找,说明会从内到外的一层层进行判断,直到最外层的布局为止。
最终会调用viewGroup的FocusFinder来找计算下一个获得焦点的view。
FocusFinder.findNextFocus
// FocusFinder.java
public final View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) {
return findNextFocus(root, focused, null, direction);
}
//root是上面isRootNamespace()为true的ViewGroup
//focused是当前焦点视图
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
View next = null;
ViewGroup effectiveRoot = getEffectiveRoot(root, focused);
if (focused != null) {
// 优先从xml或者代码中指定focusid的View中找
next = findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(effectiveRoot, focused, direction);
}
if (next != null) {
return next;
}
ArrayList focusables = mTempList;
try {
focusables.clear();
effectiveRoot.addFocusables(focusables, direction);
if (!focusables.isEmpty()) {
//其次,根据算法去找,原理就是找在方向上最近的View
next = findNextFocus(effectiveRoot, focused, focusedRect, direction, focusables);
}
} finally {
focusables.clear();
}
return next;
}
从上面可以看出
- 优先找开发者指定的下一个focus的视图 ,就是在xml或者代码中指定NextFocusDirection Id的视图
- 其次,根据算法去找,原理就是找在方向上最近的视图
根据用户指定xml去找焦点
FocusFinder.findNextUserSpecifiedFocus
先看查找用户在xml指定的目标
private View findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) {
// check for user specified next focus
View userSetNextFocus = focused.findUserSetNextFocus(root, direction);
if (userSetNextFocus != null && userSetNextFocus.isFocusable()
&& (!userSetNextFocus.isInTouchMode()
|| userSetNextFocus.isFocusableInTouchMode())) {
return userSetNextFocus;
}
return null;
}
所以看到这里是会根据View的focusable相关属性决定是否返回该View,如果不设置focusable属性,系统是不会赋予其焦点的。
View.findUserSetNextFocus
/**
* If a user manually specified the next view id for a particular direction,
* use the root to look up the view.
* @param root The root view of the hierarchy containing this view.
* @param direction One of FOCUS_UP, FOCUS_DOWN, FOCUS_LEFT, FOCUS_RIGHT, FOCUS_FORWARD,
* or FOCUS_BACKWARD.
* @return The user specified next view, or null if there is none.
*/
View findUserSetNextFocus(View root, @FocusDirection int direction) {
switch (direction) {
case FOCUS_LEFT:
if (mNextFocusLeftId == View.NO_ID) return null;
return findViewInsideOutShouldExist(root, mNextFocusLeftId);
case FOCUS_RIGHT:
if (mNextFocusRightId == View.NO_ID) return null;
return findViewInsideOutShouldExist(root, mNextFocusRightId);
case FOCUS_UP:
if (mNextFocusUpId == View.NO_ID) return null;
return findViewInsideOutShouldExist(root, mNextFocusUpId);
case FOCUS_DOWN:
if (mNextFocusDownId == View.NO_ID) return null;
return findViewInsideOutShouldExist(root, mNextFocusDownId);
case FOCUS_FORWARD:
if (mNextFocusForwardId == View.NO_ID) return null;
return findViewInsideOutShouldExist(root, mNextFocusForwardId);
case FOCUS_BACKWARD: {
if (mID == View.NO_ID) return null;
final int id = mID;
return root.findViewByPredicateInsideOut(this, new Predicate() {
@Override
public boolean apply(View t) {
return t.mNextFocusForwardId == id;
}
});
}
}
return null;
}
就是通过设置的id去找view,比如:按了“左”方向键,如果设置了mNextFocusLeftId,则会通过findViewInsideOutShouldExist去找这个View。具体怎么找的就不看了,大概是findViewInsideOutShouldExist这个方法从当前指定视图去寻找指定id的视图。首先从自己开始向下遍历,如果没找到则从自己的parent开始向下遍历,直到找到id匹配的视图为止。
根据算法自动找目标
FocusFinder.findNextFocus
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect,
int direction, ArrayList focusables) {
if (focused != null) {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
}
// fill in interesting rect from focused
focused.getFocusedRect(focusedRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focused, focusedRect);
} else {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
// make up a rect at top left or bottom right of root
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
}
break;
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_UP:
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
}
}
}
}
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
return findNextFocusInRelativeDirection(focusables, root, focused, focusedRect,
direction);
case View.FOCUS_UP:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(focusables, root, focused,
focusedRect, direction);
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown direction: " + direction);
}
}
- 遍历找出所有isFocusable的视图
- 将focused视图的坐标系,转换到root的坐标系中,统一坐标,以便进行下一步的计算
- 进行一次遍历比较,得到最“近”的视图作为下一个焦点视图
KeyEvent小结
- ViewRootImpl的processKeyEvent方法获取按键事件
- 判断ViewGroup的dispatchKeyEvent()方法是否消费了事件,是则不往下分发,终止
- 判断是否是一些特殊按键如:接听,挂断,音量等,是则不处理
- 如果没有消费事件,那么焦点就会交给系统来处理
- 开始计算记录按键的方向 direction 触发查找焦点
- 先查找当前当前持有焦点的View,DecorView会从顶部一层一层往下调用findFocus方法找到当前获取焦点的View
- 如果是View,则直接判断是否持有焦点
- 是则返回自己
- 不是返回null
- 如果是ViewGroup,先判断自己是否持有焦点
- 是则返回自己
- 不是则直接返回当前持有焦点的子View(mFocused 具体看代码分析)
- 如果是View,则直接判断是否持有焦点
- 通过focusSearch从内到外层层寻找下一个焦点view
- 持有焦点的View不会查找,而是通过parent查找,直到顶层为止,具体算法在FocusFinder
- 查找分为两种
- 优先找用户在xml指定的view
- 系统根据算法找view
小结
FocusFinder.findNextUserSpecifiedFocus会根据focusable属性决定是否使用该view,所以如果想在系统层修改使所有view都能接收焦点,这里是个修改的参考点。
另外,就是从系统层面给所有的view添加focusable属性,也就是解析的时候给view都加上这个属性。
最后就是焦点的显示,可能也需要给所有的view添加获取焦点后的放大或加边框显示。
有的我做了。


![[Android][Framework] AndroidTV小窥及keyEvent事件传递流程](/medias/featureimages/20.jpg)
![[Java] 使用EnumSet代替位运算简化代码逻辑](/medias/featureimages/6.jpg)